Blockchain wallets are crucial for securely managing cryptocurrency assets. Whether you’re a beginner or a crypto expert, understanding what is blockchain wallet can transform your digital finance journey. Explore how these wallets safeguard your funds and ensure secure transactions in the blockchain ecosystem.
What is a Blockchain Wallet?
Blockchain wallets, often referred to as crypto wallets, are digital tools that allow individuals to store, send, and receive cryptocurrencies. Imagine them as digital containers for your cryptocurrency assets, but instead of holding physical bills or coins, they hold cryptographic keys that grant access to your holdings.
A blockchain wallet is a software program that provides a secure and convenient way to manage your cryptocurrency. It serves as an interface for interacting with the blockchain, a decentralized, public ledger that records all cryptocurrency transactions.
Key Components: Public Key, Private Key, and Seed Phrase
Public Key: A public key is a publicly visible string of characters that allows others to send cryptocurrency to your wallet. It is similar to your bank account number.
Private Key: A private key is a secret code that only you should know. It allows you to access and manage your funds in the wallet and sign transactions. Keeping your private key secure is crucial for protecting your cryptocurrency.
Phrase: A seed phrase, also known as a recovery phrase, is a list of 12-48 words that acts as a backup for your private key. It is crucial for recovering access to your wallet if you lose your private key
How Blockchain Wallets Work
Blockchain wallets operate by using a unique set of cryptographic keys – a public key and a private key – that are generated and linked to each other.
The public key acts as your digital address, allowing you to receive cryptocurrency, while the private key is a secret code that grants you control over your funds and enables you to sign transactions and authorize the transfer of your digital assets. Think of it like a bank account number (public key) and a password (private key) that unlocks your account.
Key Components: Public Key, Private Key, and Seed Phrase
Public Key: A public key is a publicly visible string of characters that allows others to send cryptocurrency to your wallet. It is similar to your bank account number.
Private Key: A private key is a secret code that only you should know. It allows you to access and manage your funds in the wallet and sign transactions. Keeping your private key secure is crucial for protecting your cryptocurrency.
Seed Phrase: A seed phrase, also known as a recovery phrase, is a list of 12-48 words that acts as a backup for your private key. It is crucial for recovering access to your wallet if you lose your private key.
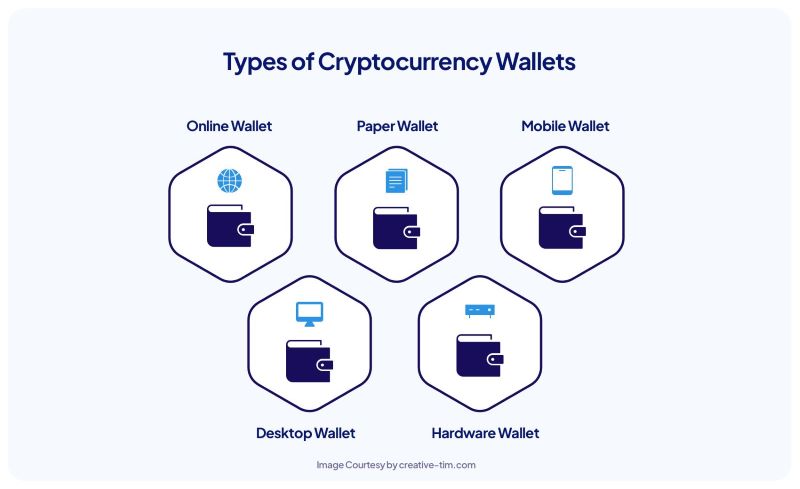
Different Types of Blockchain Wallets
Hot Wallets: Convenience and Accessibility
The cryptocurrency landscape offers various wallet types, each catering to specific needs. Hot wallets are known for their user-friendliness and accessibility, enabling swift transactions. These wallets maintain a constant connection to the internet, making them convenient for frequent trading and interactions.
Web Wallets: Binance, Coinbase
Web wallets, such as Binance and Coinbase, are readily accessible through web browsers, offering a user-friendly interface for beginners. Users can easily navigate the platform and perform transactions without needing to download any software. However, due to their online nature, they pose a higher security risk compared to offline storage solutions.
Desktop Wallets: Electrum, Exodus
Desktop wallets, like Electrum and Exodus, provide a more secure alternative to web wallets by residing on a user’s computer. These wallets offer increased control over private keys and enhance privacy. However, users must ensure their computer is protected with robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access.
Mobile Wallets: Trust Wallet, Terra Station
For on-the-go cryptocurrency management, mobile wallets like Trust Wallet and Terra Station provide a convenient means to access and manage crypto assets through smartphone apps. They offer a balance between accessibility and security, enabling users to easily send and receive crypto while maintaining a degree of control over their assets.
Cold Wallets: Enhanced Security for Long-Term Storage
When it comes to safeguarding cryptocurrency long-term, cold wallets prioritize security over convenience. They remain offline, rendering them immune to online threats like hacking attempts. These wallets are ideal for holding larger amounts of crypto for extended periods.
Hardware Wallets: Ledger, Trezor
Hardware wallets, such as Ledger and Trezor, are physical devices that store private keys offline, providing the highest level of security. Users can connect these wallets to their computers for transactions but keep the private keys physically separate from the internet. This approach minimizes the risk of theft or unauthorized access.
Paper Wallets
For ultimate offline protection, paper wallets offer a simple yet effective solution. Users can print a QR code or a string of characters containing both public and private keys, enabling secure storage. While robust against cyber threats, paper wallets require careful handling and storage to prevent physical damage or loss.
Categorizing Wallets by Cryptocurrency Support
The cryptocurrency market features a diverse range of digital assets, each operating on dedicated blockchains. This diversity has led to the emergence of wallets specialized for particular cryptocurrencies or multiple chains.
Multi-Chain Wallets
Multi-chain wallets support various cryptocurrencies across different blockchains, simplifying asset management for users holding diverse portfolios. These wallets offer the flexibility to store and manage multiple cryptocurrencies within a single platform.
Single-Chain Wallets
Single-chain wallets, as the name suggests, are designed to store and manage cryptocurrencies exclusive to a specific blockchain. For instance, Ethereum wallets exclusively handle Ethereum-based tokens. This specialization ensures optimized performance and security within that particular blockchain ecosystem.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Wallets
The world of blockchain wallets also distinguishes between centralized and decentralized systems, impacting the level of user control and security.
Custodial Wallets (Centralized)
Custodial wallets, often associated with cryptocurrency exchanges or platforms, centralize control over private keys. This means that the platform manages users’ private keys, providing convenience but potentially compromising user autonomy. Users rely on the platform’s security measures to protect their assets.
Non-Custodial Wallets (Decentralized)
Non-custodial wallets empower users with full control over their private keys. These wallets, typically mobile, desktop, or hardware wallets, enable users to independently manage access to their crypto assets. This decentralized approach prioritizes user privacy and security, as the platform itself doesn’t have access to users’ private keys.
Securely Using Blockchain Wallets
Always double-check wallet addresses before initiating transactions. A small typo can lead to irreversible loss of funds. It’s a good practice to copy and paste addresses whenever possible.
The cryptocurrency space is rife with scams and phishing attempts. Be wary of suspicious emails, websites, or social media messages promising unrealistic returns or requesting your private keys.
Secure your blockchain wallet accounts with strong, unique passwords. Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) to add an extra layer of security, requiring a second form of verification, such as a code from an authentication app, in addition to your password.
Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Consider diversifying your cryptocurrency holdings across different wallets, including both hot and cold wallets. This approach mitigates risk by minimizing the impact of a potential breach.
Regularly update your blockchain wallet software and firmware to benefit from the latest security patches and features. Outdated software can contain vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.
Create secure backups of your blockchain wallet, including your seed phrase. Store these backups in multiple, safe locations. In case of device loss or damage, a backup ensures you can recover your funds.
In the ever-evolving landscape of cryptocurrencies, blockchain wallets stand as essential tools for safeguarding your digital assets. By understanding the different types of wallets, their pros and cons, and implementing robust security practices, you can confidently navigate the world of blockchain and harness the transformative power of cryptocurrencies.
Curious to learn more about how blockchain wallets work? Follow Dynamic Crypto Network for in-depth insights and practical tips on securely managing your crypto with a blockchain wallet. Discover more today!