Unveiling Blockchain Architecture: The Foundation of Tomorrow’s Tech
You’ve heard the hype, you’ve seen the rise of Bitcoin, but what lies beneath it all? What is blockchain architecture? It’s time to dive into the nuts and bolts, to unravel the tech that may define our future. Without complex jargon, let’s break down how this system works and why it’s so powerful. From its robust design to the tech that keeps it ticking, I’ll guide you through the essentials. Get ready to uncover the core that powers a decentralized world – let’s get started on a journey into the architecture of blockchain!
Deciphering Blockchain’s Foundation: Design Principles and Technology
The Role of Blockchain Design Principles in Shaping Tomorrow’s Networks
When you think of blockchain, you might see it as a web of computers working together. At its heart lie design principles. These rules shape how blockchain grows and stays strong. Every part must work well together for the network to run smooth. Think of it like a game with rules; each player knows what to do. These rules are like invisible hands that keep the tech in check. They make sure no single party takes over and that all is fair.
Distilling Distributed Ledger Technology: More Than Just Buzzwords
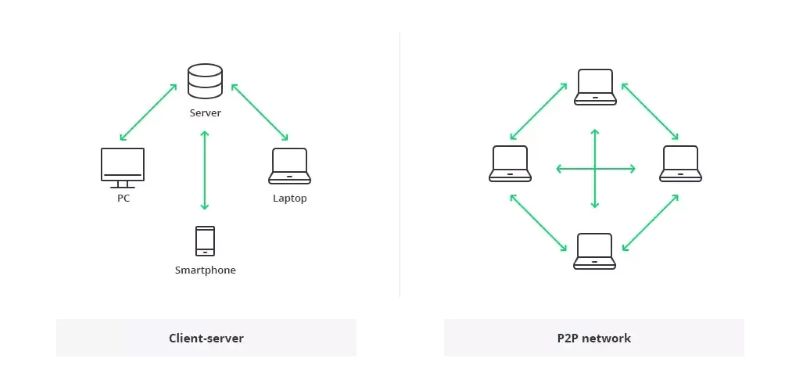
Now, let’s chat about distributed ledger technology, often called DLT. In simple words, it’s a shared, secure record of information. Picture a book that many people can write in at the same time. Once someone writes in it, no one can erase it. This book lives across a network of computers, called nodes. They all hold a copy of the book. Safe and sound, it’s hard to mess with this record. This is what makes blockchain trusty and solid.
DLT isn’t just a trendy term. It’s a real shift in keeping records that can change lots of things we do. From money to messages, it keeps our info safe for us all to use. It’s like a digital stone tablet for our modern world. If you want to know how all this works, well, it’s all about teamwork. It’s the nodes that talk and agree on what’s true. This means no single node can lie or cheat without getting caught.
This teamwork is made through blockchain components, like consensus algorithms. These are methods the nodes use to agree on what’s right. They’re like the rules of the game, telling the nodes how to reach the same answer. Smart contracts and blockchain go hand-in-hand too. They auto-run deals or tasks when certain things happen. They’re like a robot inside the blockchain, doing jobs without people needing to tell them each step.
In the crypto world, blockchain keeps us safe with cryptography. It’s a type of secret code that guards our info. Because of this code, the ledger stays unchangeable, which means you can’t rewrite history. Imagine writing with a pen that never erases; that’s blockchain for you.
Now, not all blockchains are the same. There are public ones that anyone can join and private ones that are just for certain folks. Each type fits different needs. A public blockchain is like a city park, open for everyone. A private blockchain is more like a backyard, where you choose who comes in.
TL;DR? Blockchain is made of rules and parts that let us share and protect info. It’s like a tamper-proof digital record book that reaches across the world.
Building Blocks of Blockchain: Nodes, Components, and Algorithms
The Backbone of Blockchain: Understanding Node Network Structure
In every blockchain, there are nodes. Nodes are like tiny computers that hold a copy of all blockchain data. They speak to each other to check new information. This is done to make sure new data matches the old. Nodes are what keep the blockchain secure and up to date.
Because each node stores the blockchain’s data, they can stop bad actors. Even if one node has false data, the others will reject it. They all agree on what the real data is. This makes it hard to change the blockchain without permission.
Selecting the Right Consensus Algorithm: The Heart of Blockchain Functionality
A consensus algorithm in blockchain is like a rule book. It tells all the nodes how to agree on new info that’s being added. It’s really important because it helps keep the blockchain running smoothly.
Consensus algorithms are chosen to fit what the blockchain needs. There are many types, like proof of work and proof of stake. They each have their own ways to protect the network and check transactions.
Proof of work makes nodes do hard math problems to add new blocks. Proof of stake lets nodes who have more coins or tokens help decide on new blocks. Both ways try to make sure everyone agrees on what’s true in the blockchain.
Smart contracts are another part of blockchain. They are like contracts in real life but are done by coding. When certain things happen, the contract does what it says, without anyone having to do it by hand.
Cryptography is the art of secret writing but in blockchain, it’s used to secure the data. With it, we can make sure the data has not been changed. This makes the blockchain an immutable ledger, which means once something is added, it cannot be changed or removed.
Blockchains need to store all of their data. This has to be done in a way that is quick to get when needed. It’s a big deal because if the data is hard to reach, the blockchain can be slow.
Blockchains can be public or private. Public blockchains let anyone join and take part. Private blockchains only let certain people join. They’re often used by companies who want more control over their blockchain.
Security in blockchain is a huge focus. Since blockchains are online, they could be attacked by hackers. That’s why there are many security measures to stop this from happening. These measures help people trust the blockchain more.
Every piece of data in a blockchain gets a hash function. This is like a unique code that only that piece of data will have. It stops people from making changes without being seen.
Blockchain’s data comes together to form a chain of blocks. That’s how it gets the name. Each block is like a page in a ledger or record book. The blockchain’s rules make sure these blocks are added in a way that is fair and follows the rules.
Blockchain can face problems with scaling because as more people use it, it needs to handle more data. It has to do this without slowing down or costing too much.
So, there’s a lot that goes into blockchain design. We didn’t even talk about all of it yet. But now you know some of the key parts that make it work. These include nodes that keep a record, the rule book that tells them what to do, and the ways they keep everything secure and honest.
Ensuring Trust and Efficiency: Smart Contracts, Security, and Storage
Crafting the Smart Contract Layer for Seamless Integration
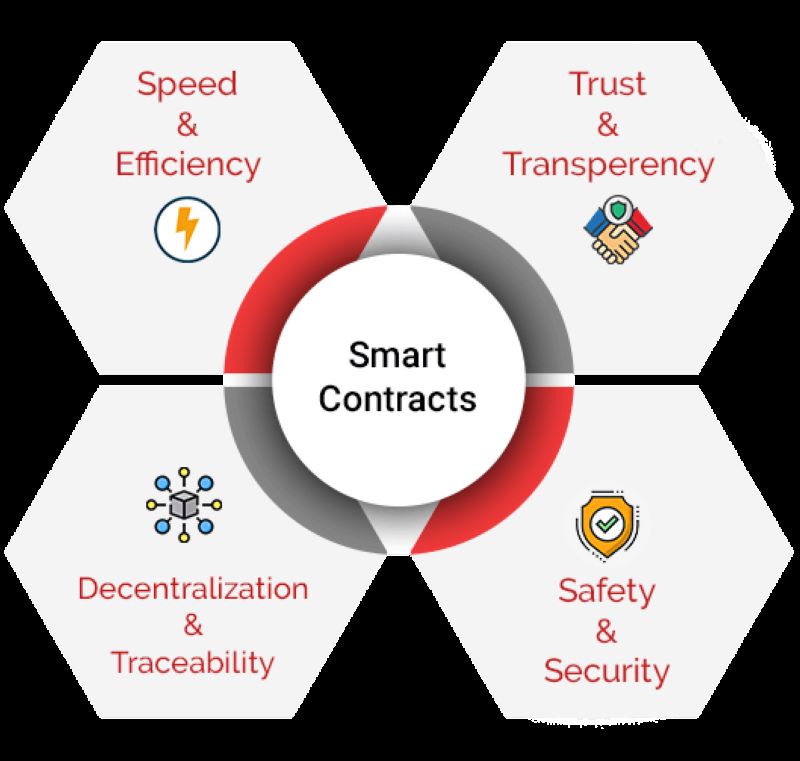
Smart contracts are like robot promises. They make sure deals go as planned. When two people want to trade, smart contracts step in. They check the rules and do the trade with no need for a middleman. That’s cool because it’s quick and no one can cheat.
Now, let’s get to how they fit into blockchain. Each blockchain has parts that work together. Smart contracts are one key part. They look at the info and decide, “Should this trade happen?” If everything checks out, they say “Yes,” and the trade is done.
But for everything to work smooth, smart contracts must be built right. Think of it like LEGO. If you follow the instructions, your LEGO castle stands strong. Smart contracts need clear rules to work well. This way, they can do their thing and you can trust them.
Balancing Decentralization and Security: Cryptography and Data Storage Solutions
Okay, so we’ve got all these computers holding the same info. That’s what we call a node network. It’s a bunch of pals sharing their notebooks to make sure no one cheats on the test.
Now, here’s where things get ninja-level. We use secret codes, called cryptography, to keep everything safe. Nobody can mess with the info if the codes are good.
An immutable ledger is like a diary with super glue on the pages. Once you write in it, it’s stuck for good. That means no one can sneak in and change stuff.
And we need a place to keep all this info. That’s what we call blockchain data storage. It’s like a giant toy box where every toy has a place. This keeps our info easy to find and safe.
Public blockchains are like parks. Everyone can come in and play. Private blockchains are more like your backyard. Only friends and family — people you know — can join.
We keep our blockchains safe with cool things called hash functions. They make sure every block fits just right. If a block doesn’t fit, it’s a no-go. This keeps cheats out.
Now, let’s not forget how we talk in our node network. We whisper to each other using peer-to-peer chat. No need for a loudspeaker. It’s like passing notes in class, but super secure.
For all this to work, we need strong security measures. We’re like cyber guards, always watching for sneaky bugs or hackers. This builds a big wall of trust around our blockchain.
So, what did we see today? Smart contracts make deals safe and fast. Cryptography is our secret code for safety. And we keep our blockchain blocks neat and tidy in our storage. All this, together, means we can trust the blockchain to be our buddy in the tech future.
Expanding Blockchain Horizons: Scalability and Governance
Tackling Scalability Concerns to Future-Proof Blockchain Networks
As a blockchain architect, I face a big challenge: making sure blockchain can grow. Scalability is like a busy highway getting more lanes. On blockchains, more transactions mean we need bigger roads. But how can we do that without causing trouble? We work on ways to make the road bigger without making traffic jams. This means thinking of new designs. We tweak blockchain rules to process more data fast. It’s about smart upgrades for a better blockchain highway.
From Rules to Execution: Implementing Effective Blockchain Governance Models
Now, let’s talk about making rules in blockchain. Governance is all about the who and how in rule-making. It’s like deciding the game rules before playing. In blockchain, everyone playing must agree on changes. This means setting clear rules for how we vote on updates. We’re aiming for a fair, open system where each voice matters. Remember, making choices in blockchain isn’t just about today. It’s about keeping the game fair for years to come.
We’ve just dug deep into the world of blockchain, starting from the core design principles all the way to its scalability and governance. First, we learned that good design is key to networks that last. Then, we moved on to the building blocks, seeing how nodes and the right algorithms keep everything ticking.
On top of that, we discovered that smart contracts, when done right, make deals smooth and trustworthy. Security is also a big deal, and we found out how encryption and smart storage choices help keep our data safe.
Finally, we looked at how blockchain can grow big while still working well, and how having clear rules helps everyone play fair. All this tech talk might seem complex, but it’s all about making networks we can count on. And guess what? That’s the blockchain’s superpower – creating a future where we trust the tech in our lives. So, keep these points in your toolkit as we ride the blockchain wave together!
Q&A :
What is meant by blockchain architecture?
Blockchain architecture refers to the structured framework that combines various elements such as decentralization, cryptography, and consensus mechanisms, laying down the fundamentals for creating a secure and dependable blockchain system. The architecture establishes how data is organized, how transactions are processed, and how different users can access the information stored on the blockchain network.
How does blockchain architecture ensure data security?
Blockchain architecture utilizes advanced cryptographic techniques to ensure data security. Each transaction is encrypted and linked to the previous transaction, forming a chain that is nearly impossible to alter. The distributed ledger design means copies of the ledger are held on multiple nodes across the network, which makes tampering with the data very difficult, as the majority of nodes need to validate any changes collectively.
What are the key components of blockchain architecture?
The key components of blockchain architecture include:
- A distributed ledger that records all transactions across multiple nodes.
- Cryptography which ensures secure transactions and records.
- A consensus mechanism that validates and agrees upon the state of the ledger.
- Smart contracts that enable the automation of processes and agreements within the blockchain.
- Nodes which are the individual computers connected to the blockchain network that participate in its maintenance.
Can blockchain architecture be scaled for large-scale applications?
Blockchain architecture can be scaled for large-scale applications though it often requires innovations or adaptations, such as the use of off-chain transactions channels, sharding, and layering solutions, to improve transaction speeds and data handling capacities. Researchers and developers are constantly working to enhance the scalability of blockchain to support larger ecosystems like financial transactions, supply chain management, and more.
What distinguishes blockchain architecture from traditional database architecture?
Blockchain architecture is distinctive because it emphasizes complete decentralization and transparency. Unlike traditional database architecture where the data is typically managed by a centralized authority, blockchain distributes the data across a network of nodes. This ensures that the ledger is immutable as every node in the network keeps a copy of the transactions and consensus is required for updates, creating a trustless environment that doesn’t rely on a central point of control.