Dive deep with me as we explore the bedrock of crypto tech – what is a layer 1 blockchain. This tech shapes how we trade, invest, and secure digital assets today. Knowing its core is not just for tech wizards; it’s vital for anyone in the digital space. Trust me, I’ve been around blockchains enough to tell you, understanding the nitty-gritty of Layer 1 is a game-changer. Let’s peel back the layers and decode why this innovation is more than just a tech buzzword.
Unveiling the Fundamentals of Layer 1 Blockchains
Defining the Layer 1 Blockchain
Let’s talk straight about layer 1 blockchain. You might ask, “What’s a layer 1 blockchain?” Simple. It’s the base level of blockchain technology. Imagine it as the ground floor of a building. Everything starts here. It’s where all the data lives. You could say it’s the heart of blockchain. This base layer holds every bit of info that goes through it.
Think of blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum. They’re both great examples of layer 1 blockchains. If we didn’t have them, we wouldn’t have all the cool blockchain stuff we have today. They’re the big bosses that start the show.
The Significance of Blockchain Fundamentals
Now, why should you care about blockchain basics? Because they are what make blockchains tick. These basics include how things get added to the blockchain, how safe it is, and how all the hard math stuff keeps the network running smooth.
Blockchain tech is clever, and it’s changing how we do lots of things, like sending money and signing contracts. It cuts out the middleman. No banks or lawyers needed here, which is pretty cool if you ask me.
And there’s more to it. Like how new coins are made and how everyone who helps the network gets some coins too. This is all thanks to the fancy rules of the network called consensus mechanisms. The most famous ones are called Proof of Work and Proof of Stake. They’re like the big wheels that keep everything going.
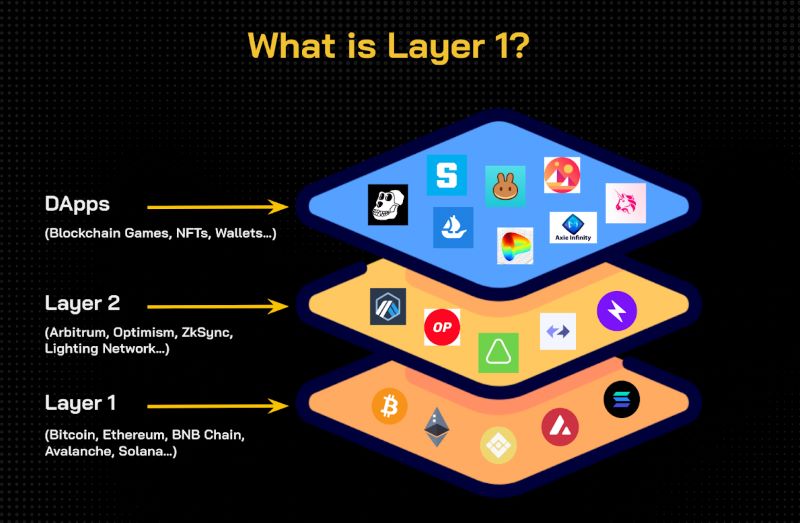
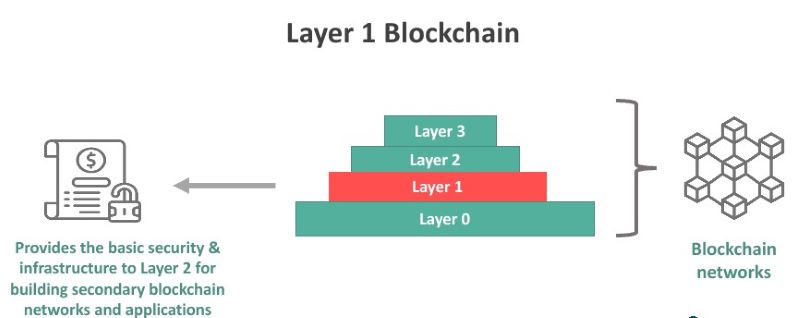
But like all things, there are some kinks to iron out. I’m talking about scalability – basically, making sure the blockchain can handle lots of people using it without getting slow. And there’s this big debate about layer 1 vs layer 2 solutions. Layer 2 is like adding another floor to our building to make more room.
One more thing – network security. It’s super important because no one wants hackers messing up their stuff. It’s all about keeping your coins and your data safe.
Now, remember on-chain transactions? They are deals that happen right on the blockchain and stay there forever. Pretty neat for keeping a clear record of everything. The more you understand layer 1 solutions, the better you get how this all fits together.
Lastly, smart contracts are a big deal on layer 1. They are like deals that can think for themselves. Say you buy something, and once it’s sent, the payment goes out. Automatic and easy, right?
So, as we pull back the curtain on the layer 1 blockchain, we see it’s not just tech talk. It’s a new way to look at money, deals, and trust. And it’s exciting to think about where it will take us next.
The Architecture and Infrastructure of Layer 1 Blockchains
Exploring Blockchain Architecture and Infrastructure
Let’s dive into how layer 1 blockchains work. They are the base of all blockchain tech. Think of them like the foundation of a house. They hold everything up. First, we’ve got the blockchain. It’s a chain of blocks, right? Each block carries a bunch of transactions. It’s like a digital ledger that keeps track of who sent what to whom.
This ledger lives across many computers. This setup means the records are hard to change once written. We call that decentralized network. It’s a team sport with no rule by a single player. Next, we tackle consensus mechanisms. They are rules for trust among strangers. Proof of Work and Proof of Stake are the biggies. With Proof of Work, think of miners digging for digital gold, using power. Proof of Stake is like holding a lottery ticket in the form of coins, using less power.
Understanding layer 1 solutions means seeing these blockchains as the main chain, or mainnet. They are the first and main place for transactions to live on a blockchain. They support smart contracts too. That’s code that self-runs when terms are met. It’s like a vending machine that delivers soda when you insert a coin.
Validation of transactions? That’s like a guard checking your entry badge. And network security? That’s keeping out the unwanted dudes from crashing the party.
Let’s push this further. Scalability solutions are tweaks for the blockchain to handle more action, faster. We live in a fast world and blockchains must keep pace. Then mainnet – it’s the real deal, where actual transactions ride the blockchain.
Use Cases: Examples of Layer 1 Blockchains
Now for some star examples of layer 1 blockchains. You’ve probably heard of Bitcoin and Ethereum. They’re like Coke and Pepsi in the world of crypto. They’ve got fame and were first to party in the crypto world. Bitcoin uses Proof of Work to mine new coins. Ethereum started there too but is moving to Proof of Stake.
Now, what about the layer 1 vs layer 2 talk? Layer 2 is an add-on to help layer 1 scale up. It’s like adding a new floor to that foundation we mentioned. But here, we’re focusing on layer 1 — the groundwork.
Why these blockchains matter? Layer 1 infrastructures are the muscles and bones of blockchain. Not only do they carry out and record transactions, but they also set the rules on how things run.
Investing in layer 1 assets? Know the game. Check out layer 1 tokenomics. It’s all about how coins are made, used, and what they’re worth. Mining on layer 1 is like a digital treasure hunt. You use power and brainwork to bag new coins.
Layer 1 blockchains are homes to cryptocurrencies. They offer first-level solutions on which everything else in crypto is built. It’s the core of blockchain technology where all the action kicks off. A sturdy layer 1 means a stronger, safer home for digital coins.
Delving into Layer 1 Consensus and Security
Understanding Consensus Mechanisms: PoW and PoS
Let’s dive into the heart of blockchain tech – how it agrees, or reaches “consensus”, on true transactions. When we talk about consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), we’re talking about the rules that keep everyone on the same page.
Think of PoW as a tough math contest. It requires super strong computers to solve complex problems to add new blocks to the chain. It’s the original rule book used by Bitcoin. It’s a bit slower and uses more power, but it’s proven to work.
Now, PoS is like a raffle where your tickets are the coins you own. The more you have, the better your chances to get picked to approve transactions and get rewards. It’s faster and saves energy, making it a rising star in blockchain tech.
Both these rules help make sure everything is fair and safe without needing a boss to watch over.
Prioritizing Network Security in Decentralized Networks
Staying safe is a big deal on decentralized networks. Nobody owns these networks, so everyone needs to follow the rules. It’s like a neighborhood watch, but for internet money.
Network security keeps our digital bucks from getting stolen. It stops cheaters and makes sure all plays are fair. You can’t rewind or make easy edits on a blockchain. Once something’s in there, it’s like carving into stone.
This toughness is why we trust it with our money, messages, and even digital collectibles. Each change on the ledger must be approved by majority rule – kind of like a group thumbs-up.
In the wild world of crypto, where everyone is trying to make a buck, strong security is a must-have. And that’s something layer 1 blockchains take really seriously. They lay the foundations for trust and keep the digital neighborhood safe.
Remember, both PoW and PoS have a common goal: to come to an agreement on what is true across all computers connected to the network. And without a solid agreement process, our digital coins are just make-believe. It’s the tough rules of PoW and the clever lottery of PoS that make blockchain tech trustworthy and exciting.
But hey, don’t just take my word for it. The constant hustle of brilliant minds is always pushing the boundaries of what these networks can do. And it’s these layer 1 solutions that make sure we all play by the rules and keep our digital world secure.
Layer 1 Blockchain Scalability and Interoperability
Challenges and Solutions for Blockchain Scalability
Have you heard of “blockchain scalability” and wondered what it’s about? It’s how many actions a blockchain can do in a short time. Think of it like a road. If there are too many cars, traffic jams happen. In blockchains, too much traffic slows everything down.
One big problem for Layer 1 blockchains is handling more action without losing speed. Bitcoin and Ethereum are two Layer 1 blockchains. Their early designs didn’t think we’d be using them so much.
What are people doing to fix this? Here’s where “scalability solutions” jump in. They’re like adding more lanes to a highway or finding new paths. Developers improve code and make changes in how these blockchains check transactions. They create new rules to decide which transactions happen first.
Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) are ways blockchains agree on what’s true. PoW uses a lot of energy. But PoS doesn’t, so it’s like a “green” choice for blockchains.
Another idea is called “sharding.” Imagine cutting a big task into tiny jobs. Each part is simpler and faster alone. Sharding can make blockchains run better, like having many small roads instead of one big one.
Advancing Interoperability Among Blockchain Protocols
Now, what about “interoperability”? This word means different blockchains talking to each other. Just like friends from different places, blockchains should share and understand. Right now, it’s like they speak different languages.
To fix this, imagine a translator that helps blockchains chat. That’s what interoperability in blockchains is like.
But why do we want this “chat”? It’s because there’s power in joining forces. If Bitcoin’s blockchain can shake hands with Ethereum’s, we can do more with them together.
How do we make this happen? Teams work on “bridges.” These bridges let cryptocurrencies visit and work on other blockchains. They’re like customs officers, checking who comes in and out.
Making all this work is tricky, but necessary for a better blockchain world. It helps make Layer 1 blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum more useful.
My role in this big blockchain world is to think up ways to let these digital places link up. It’s about building bridges, not walls. And we do it, piece by piece. Because in the end, what we want is a smooth road for everyone, making blockchain better for you and me.
In this post, we peeled back the layers of Layer 1 blockchains. We kicked off by defining what they are and why they matter. Then, we dove into their design and how they’re built. Real-life uses showed us how these networks change our world.
Next, we dug deep into consensus and security. We learned that how a network agrees on transactions can affect safety and trust. Moving on, we tackled big issues like scale and working with other systems. We looked into hurdles and fixes, aiming to make these blockchains fast and wide-reaching.
Wrapping up, Layer 1 blockchains are vital. They are the bedrock of crypto. They must keep growing to support more users and new ideas. They face challenges, sure, but the future seems bright with all the smart folks working on better tech. As we keep pushing for faster and safer networks, we’re on the edge of a digital shift that will stir up tech as we know it. It’s an exciting time to watch and be part of the change.
Q&A :
What is a Layer 1 Blockchain?
A Layer 1 blockchain refers to the foundational infrastructure of a blockchain network. It encompasses the core framework that supports the creation of a decentralized ledger, capable of recording transactions and managing the issuance of new tokens or coins. This base layer is critical for ensuring security, scalability, and consensus across the network.
How Does a Layer 1 Blockchain Operate?
Operationally, a Layer 1 blockchain utilizes a consensus mechanism such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) to validate transactions and create new blocks. Nodes running the blockchain’s protocol work together to maintain the integrity of the ledger, with inbuilt mechanisms ensuring that all data recorded on the chain is accurate and tamper-proof.
What Makes Layer 1 Different From Layer 2 Solutions?
Layer 1 blockchains serve as the main platform for processing and storing transactions. In contrast, Layer 2 solutions are built on top of Layer 1 blockchains to enhance transaction speed and scalability. They handle processes off-chain before confirming them on the main blockchain, thereby alleviating congestion and reducing fees.
Can Layer 1 Blockchains Scale to Meet Demand?
Scalability has been a significant challenge for Layer 1 blockchains, especially for those using PoW like Bitcoin. However, there are ongoing developments, including upgrading consensus mechanisms and introducing sharding techniques, which are designed to increase transaction throughput without compromising security.
What Are Examples of Layer 1 Blockchains?
Some leading examples of Layer 1 blockchains include Bitcoin, Ethereum, Cardano, Binance Smart Chain, and Solana. Each offers a unique framework and consensus mechanism, shaping their respective strengths in terms of security, scalability, and network capabilities.