Margin Trading on Crypto Exchanges: Unpacking the Real Costs
Imagine diving deep into crypto, where every dollar counts, and the term fees for margin trading on crypto exchanges looms large. You’re in it to make a profit, but the costs can nibble at your earnings like a mouse in a cheese shop. Let’s cut through the fine print! I’ll walk you through the real costs of margin trading, not just the big, flashy numbers. We’ll break down leverage, spot hidden fees, and compare platforms. You’ll learn strategies to keep fees low and profits high. Buckle up; it’s time to master the art of trading smart!
Understanding the Basics of Margin Trading Economics
The Functionality of Leverage in Crypto Trading
Leverage is a tool in crypto trading. It lets you trade more than you have. Think of it as borrowing money to invest more. If you’re right, you win big! But be careful. If you’re wrong, you can lose a lot, fast.
Crypto exchanges let you use leverage. This means you put down a small amount of money. It’s called ‘initial margin’. Then, the exchange loans you the rest. This can boost your gains. Yet, the flip side is it can also boost your losses.
Leverage levels vary a lot. Some exchanges offer 2x, 5x, or even 100x the money you put in. More leverage means higher risk. Always remember this. It’s tempting to go for big gains. But it’s also easy to lose your money.
Distinguishing Different Types of Margin Fees
Fees for margin trading can be tricky. They can eat into your profits. Let’s unpack them.
First, every time you trade, you pay ‘commission rates’. This fee is for using the platform’s services. Second, when you borrow, you pay ‘interest rates’. Think of it as the cost of renting money.
There are ‘funding rates’. You pay these daily or hourly. It depends on the exchange. These keep the leverage markets in line with regular markets.
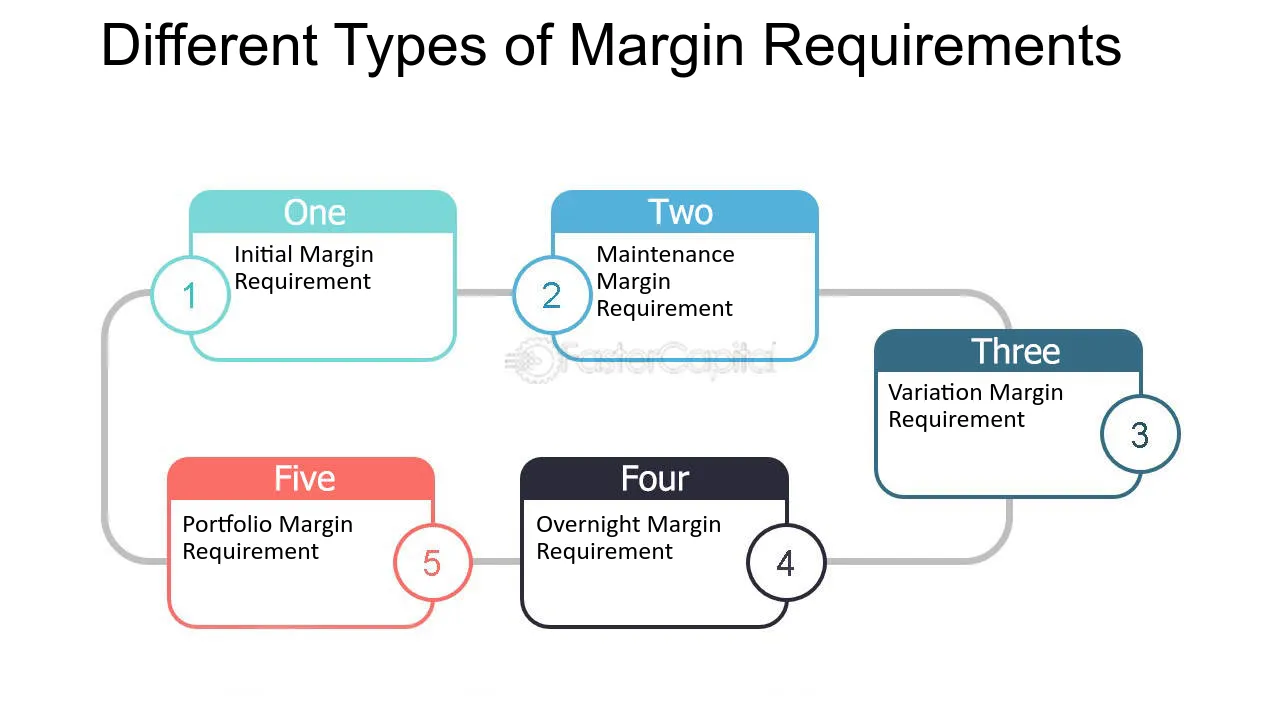
Then, we have ‘initial margin’ and ‘maintenance margin’. They are like safety nets. They make sure you have skin in the game. If the market drops, these margins protect you and the exchange from big losses.
But there are more costs if things go south. A ‘margin call’ means the exchange wants more cash or coins as cover. If you can’t pay up, you get a ‘liquidation fee’. The exchange sells your assets to cover the loan.
Now, not all fees are in plain sight. Some fees hide. Like ‘hidden fees’ for moving money around. Or for holding a position overnight. It’s called ‘overnight funding rates’. They can add up!
Short selling has fees too. It’s when you bet a crypto’s price will fall. But it comes with risks.
Cross and isolated margin fees also come into play. They deal with how you manage separate trades. Cross margin spreads the risk across all trades. Isolated margin locks the risk to one trade.
Lastly, ‘tiered margin fee structures’. They can change how much you pay. The more you trade, the fees could get lower. Or sometimes, higher. It depends on the rules of the exchange.
Making sense of fees is no small task. But it’s vital for smart trading. Knowing what you’ll pay helps you figure out what you could earn. Or lose!
In short, the cost of margin trading is not just what you might gain or lose in your trades. It’s also the fees you pay. These fees can change based on how much you borrow, how long you hold a trade, and what the exchange policies are. It’s crucial to know these fees to trade wisely. They can make the difference between profit and loss. Understanding them is the first step to successful margin trading.
Calculating the Real Cost of Margin Trading
The Math Behind Margin Fee Calculation
Let’s get down to brass tacks. When we trade on margin, we borrow money. That’s not free. Just like any loan, we pay interest. The more we borrow, the more we owe. Crypto exchanges make a buck this way. They charge fees for the service. How? They use a percent of what you borrow. This percent can change a lot between exchanges.
Say you start with $100. You choose 10x leverage. Now you’re trading $1000 worth. Think of it like this: $900 isn’t yours. You’re borrowing it. Each exchange has rates. They say, “Hey, this is what it costs to borrow from us.” So, when picking an exchange, compare their rates. It’s crucial. High fees can eat your gains. Low fees can mean more money in your pocket.
But that’s not all. We pay fees on open trades too. Some fees are daily. Others might happen overnight. A trade open for days? The fees stack up. You need to watch them. They can turn wins into losses, fast.
Assessing Initial and Maintenance Margin Requirements
Initial margin is what you first put down. It’s your stake in the game. The exchange says, “Ok, you gotta start with this much.” This is to open your trade. It’s important. The more you put down, the less you borrow. Less borrowing equals less fees.
Now let’s chat about maintenance margin. You gotta keep a minimum amount in your account. It’s like a safety net. The market moves a lot. If your account dips too low, you get a margin call. This means, “Hey, put in more money or we close your trade.” Not fun. If they close it, there could be extra fees. And if the market crashes hard your losses could be more than your stake.
Remember, each exchange has different rules. They’re like different banks with their own terms. You need to read these terms carefully. Know their initial and maintenance requirement. This helps you avoid surprises. Surprises in trading? Not usually good.
Short selling? That’s a whole other beast. You bet on prices dropping. But the fees are higher. There’s more risk. Exchanges know this. They charge more because they risk more.
Liquidation fees? That’s when your trade gets closed without your say. It means you didn’t meet the maintenance margin. The exchange has to protect itself. They sell your assets, often at a loss. And yep, they charge a fee for it.
Keep all this in mind before your next trade. Fees can be sneaky. They can turn your trade around. Or leave you owing more than you thought. So do your homework. Compare. Calculate. Then, trade smart.
Comparing Fee Structures Across Crypto Exchanges
Leveraging Trading Fee Comparison
When you trade with leverage on crypto exchanges, you first need to ask, “What will it cost me?” Each platform has its own set of fees, and it’s key to understand these before you start. Think of each crypto exchange as a unique store. In one store, a bread loaf might cost a dollar, while in another, the same loaf could cost two. Crypto exchanges work similarly with their fee structures for margin trading. If you’re keen on finding the best deal, comparing these costs is a must.
Analyzing Commission and Liquidation Fees on Various Platforms
Now, let’s dive into commission fees. These are like service charges, a small cut that exchanges take each time you open or close a trade. You might see a number like 0.2% per trade. That means for every $1000 traded, you’ll pay two bucks. This might seem small, but trade often and it adds up fast.
Next, there’s the beast of liquidation fees. These are what you pay if your trade hits the wrong note and your position is closed by the exchange to stop further losses. These fees can vary wildly from one platform to another. Getting to know these can save your wallet big time in a bad situation. Just remember, the higher your leverage, the closer you are to that liquidation point. It’s like walking a tightrope; the higher up, the bigger the fall.
Margin calls? They’re like a warning buzzer. They happen when your account’s value falls too much and the exchange says, “We need more money to keep your trades open.” If you can’t meet that margin call, you might face liquidation, which is when the exchange sells your assets to cover the trade—ouch.
Then there’s the daily upkeep—interest rates on what you borrow. When you trade on margin, you’re borrowing money. Kind of like using a credit card for your trades. And just like a credit card, there’s interest. Each day you keep a trade open, you’ll pay a bit more. Sometimes it’s a fixed rate; other times, it’s a rate that changes with the market—like the weather but for your wallet.
Finally, let’s not forget about initial and maintenance margin. Think of initial margin as the entry fee—how much you need to put down to start. Maintenance margin is the minimum amount you need to keep in your account. Drop below that, and it’s margin call time again.
In a nutshell, before you jump into the margin trading pool, take a hard look at the fee calendar—commission rates, interest charges, initial margins, and maintenance costs. They can all make or break your trading game. Remember that the goal is to work smarter, using knowledge of fees to craft a strategy that keeps more money in your pocket.
Strategies for Managing Fees and Maximizing Profitability
The Role of Funding Rates and Interest in Trading Strategy
Funding rates matter a lot. They tie to the cost of holding positions. Exchanges use them to balance the market. They change depending on market demand for leverage. When lots go long, the rate can get high. This adds to your trading costs. It’s what you pay or earn for holding a leveraged position.
Interest rates on what you borrow add up too. The more you borrow, the more you pay. Rates differ across platforms. Check them before you trade. Aim for low rates to keep costs down. High rates eat profit fast.
To win at margin trading, think about both. Keep funding rates and interest low. Swap out of positions before rates go up. Study when the funding rate changes. It’s key to saving money while trading with leverage.
How to Navigate Cross Margin vs. Isolated Margin Fees
Cross margin and isolated margin seem tricky. But they’re not too hard to get. Both manage your risk in different ways.
Cross margin uses all your money in one pot. This lowers the chance of liquidation. But, if it goes wrong, you lose it all. All your trades are at risk.
Isolated margin protects by setting aside money for one trade. If liquidation hits, you only lose that one trade’s margin. It keeps other trades safe. Yet, each trade might need more margin.
Fees are part of this too. Lower fees mean less money spent on each trade. This shields your profit. Always check fees for both options on the exchange. Choose what works for your plan and risk level.
Cross margin could be cheaper for less trades. Take care though! It can risk more of your money. Isolated margin might have higher fees. Yet, it can save your other trades if one fails.
What’s best? It depends on your trades, how much risk you want, and the fees. Some traders mix both. They use cross margin for steady trades. Isolated margin handles the riskier plays.
Remember, fees can cut your gains. Look for the best balance. Fees should not be too much of your trade’s value. Some fees can change fast. Keep an eye out and adjust on the go.
To sum it up, funding rates, interest, and fees are big in your trade strategy. Choose well to steer clear of nasty fee shocks. Check rates before you trade. Keep updating your plan. This way, you can trade smart and save money.
To wrap it up, we’ve taken a dive into margin trading’s nuts and bolts. We’ve seen how leverage boosts our buying power in crypto trading and pinpointed the key fees involved. Crunching the numbers, we figured out how to calculate the real hit to our wallets from margin fees and looked closely at how much we need to start and keep trades open.
We also compared what it costs to trade across different crypto exchanges. Knowing the fees inside-out can help us pick the best platform. Finally, we tackled strategies to manage fees so we can keep more of our hard-earned cash and bump up our trading game.
Remember, knowing these tricks can make or break your success in margin trading. Use what you’ve learned here to trade smarter and keep your profits high. Stay sharp out there!
Q&A :
What are typical fees associated with margin trading on cryptocurrency exchanges?
Margin trading fees on crypto exchanges can vary widely and typically include interest on the borrowed funds, opening and closing trade fees, and sometimes maintenance charges. The interest rate is usually a percentage of the amount borrowed and can be charged hourly or daily. It is crucial to understand the fee structure of the specific exchange as these fees can significantly impact the profitability of your trades.
How do exchanges calculate fees for margin trading?
Fees for margin trading on cryptocurrency exchanges are typically calculated based on several factors; the amount of leverage used, the size of the position, the length of time the position is held, and the exchange’s specific fee rates. Interest rates are applied to the borrowed funds and can be charged on a rolling basis. Additionally, there may be standard transaction fees that are applied when the position is opened and closed.
Can fees for margin trading on crypto exchanges change over time?
Yes, fees for margin trading can change over time due to updates in the exchange’s policies, shifts in market conditions, or changes in the underlying interest rates that affect borrowing costs. Crypto exchanges may update their fee structures in response to market volatility or changes in the competitive landscape. Therefore, it’s essential for traders to stay informed about the latest fee schedules on the exchanges they use.
Are there any ways to reduce fees for margin trading on cryptocurrency exchanges?
To reduce fees for margin trading, traders can look for exchanges that offer lower interest rates or reduced fees for higher trading volumes. Some exchanges also have tiered fee structures that decrease fees for users with larger monthly trading volumes. Additionally, using native exchange tokens for transaction fee payments sometimes results in discounts.
Is it possible to find fee-free margin trading on crypto exchanges?
While it’s rare to find completely fee-free margin trading on crypto exchanges, some platforms may offer temporary promotions with reduced fees or interest-free borrowing to attract new users or encourage trading. It is, however, important to be cautious and read the fine print, as there may be other costs or risks associated with these promotions.