Diving into the world of crypto, you’ve likely heard a buzz about blockchain layer 1 vs layer 2. But what does that really mean? Think of it this way: layer 1 is the ground floor, the base where everything starts. It’s your Bitcoin, your Ethereum—the roots. Yet, as the demand grows, these blockchains face a big challenge. They need to handle more and more people without slowing down. That’s where layer 2 jumps in. It’s like adding express elevators to a busy skyscraper. Quick, efficient, and game-changing. In this post, I’ll break it all down for you. We’ll explore how they work, where they shine, and why knowing the difference matters. Ready to get a clear view on this complex topic? Let’s roll.
Understanding the Foundation: Layer 1 Blockchains
Layer 1 Blockchain Examples and Their Core Functions
Let’s talk about layer 1 blockchains. They are like big digital roads where all crypto travels. Think of Bitcoin and Ethereum. They’re the main roads in our crypto city. Here, lots of cars (transactions) drive around. As more cars come in, traffic can get crazy!
Layer 1 blockchains need to handle more action without causing jams. To do this, they use special tricks. These tricks make sure all cars can move fast and safe. Now, let’s see how they do that.
Consensus Mechanisms and On-Chain Scalability
For a blockchain to work well, everyone needs to agree on the rules. This is where consensus mechanisms shine. They are like traffic lights on our roads. Some common ones are Proof of Work and Proof of Stake.
Proof of Work, used by Bitcoin, makes miners solve hard puzzles to add new blocks. It’s secure but can be slow when traffic is heavy. And it uses a lot of power.
Proof of Stake is another way to keep the road safe. It lets people who own more crypto take charge of adding new blocks. It can be quicker and uses less power than Proof of Work.
But sometimes, the road gets too packed. That’s when layer 1 scalability solutions kick in. They are plans to help move cars faster without needing more roads. We can widen the lanes or make the cars smaller so more can fit.
Think of Ethereum’s upgrade to Ethereum 2.0. It’s like a big roadwork project. It will move from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake to clear out traffic. That means faster rides for everyone without hurting the planet.
In the end, the goal is simple. We want our crypto to zip around without any hold-ups. And to make sure no one cheats, everything stays safe.
Remember, a happy blockchain is one where all cars can flow smoothly. Whether it’s a quiet Sunday drive or rush-hour madness, the road rules keep us all moving just right. Let’s keep building better roads and smarter cars for our digital city!
Layer 1 vs Layer 2 Fees and Transaction Speed
Analyzing Costs: How Layer 1 and Layer 2 Fees Differ
Let’s get right into it. The big question: Are layer 1 fees higher than layer 2 fees? Yes, often they are. Layer 1 networks can get really crowded. With more people and dApps, fees tend to go up. It’s like a busy coffee shop. More folks want coffee, the longer you wait, and sometimes, the more you pay.
Layer 1 is the main game—where the blockchain starts and lives. We call it the base layer blockchain. When a lot of users send transactions, or play games, or trade on this busy layer, it gets packed. This jam—the blockchain bottleneck—it makes fees rise as everyone fights to get their transactions through.
But here comes layer 2 to the rescue! These are like special tracks built next to the main train line. Layer 2 scaling allows transactions to happen off the main track. It means less waiting and lower fees. Think of it as a fast-pass lane where you can dodge the long lines. These solutions use sidechains, plasma, and state channels to whisk transactions away from the crowd.
So now you see, layer 2 often has lower fees ’cause it spreads the load and uses cool tech to speed things up. It’s a savvy way to save your coins and smile more, all while getting your crypto business done.
The Race for Efficiency: Layer 1 vs 2 Transaction Speed Comparison
When we talk speed, we’re eyeing how fast a transaction can happen. With layer 1, speed’s not always top-notch. Remember the crowded coffee shop? Same story. More orders mean you wait longer for your double-shot espresso.
Layer 1 blockchains can only handle so much at once. Their transaction throughput—how many transactions they can drink down each second—is limited. We see this in Bitcoin and Ethereum, two well-known layer 1 blockchain examples. Sometimes making or getting payments can feel like waiting for water to boil.
Now, blast off to layer 2, where it’s all about zipping transactions to the finish line. We’ve got state channels that open a direct line between two people. No more waiting for each step of the way. And rollups? They bundle lots of transactions into one deal and resolve them quicker than you can tie your shoes.
Ethereum scalability has got a helping hand from these techs. Layer 2 solutions comparison shows they’re winning the race against old-school layer 1 speeds. The result? You get to do more in less time. It’s like swapping out your old bike for a rocket. Next stop: the moon, with all your transactions settled before you can say “blockchain!”
Alright, pals, that’s the scoop on why people are chatting up layer 2. Layer 1’s got the security and trust; it’s true. But when you’re talking about saving time and coin? Layer 2’s the shiny new toy that’s not just cool to talk about — it actually delivers. Keep in mind, not all solutions are made the same, and your mileage may vary. It always pays to look before you leap in the crypto world!
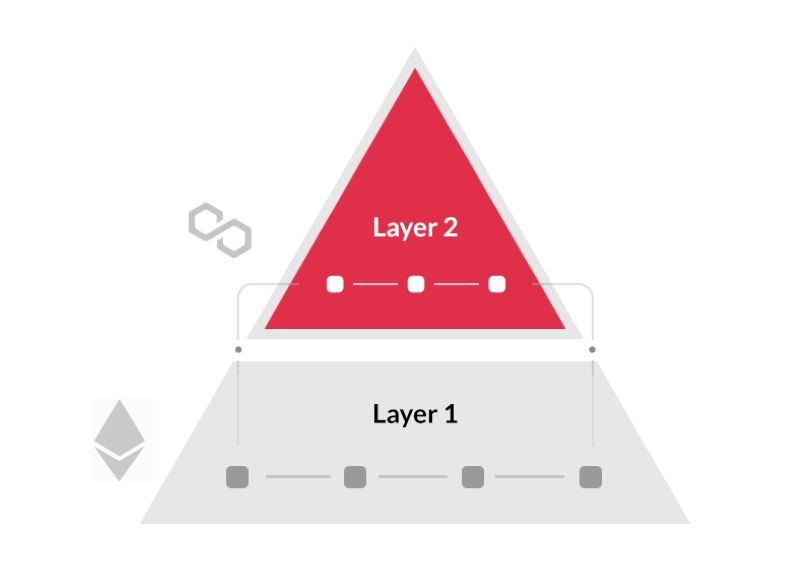
Layer 2 Scaling Solutions and Their Integration with Layer 1
Overview of Layer 2 Protocols and Off-Chain Solutions
Layer 2 scaling saves the day for many blockchains. Imagine you’re at an arcade. The arcade games are like layer 1. But there’s only one, and the line is huge. Then comes layer 2, a whole bunch of new games. Way more fun, right? Everyone can play without long waits.
So, let’s dive into how these layer 2 protocols help. They work on top of layer 1, like the extra games in our arcade. But they’re more than just extra space. They’re super smart ways to handle lots of actions, without stuffing them all into layer 1. Think of it like this: If you’re eating a burger and fries, you don’t want them all in one bite. You’d eat the fries separately, right? Layer 2 lets blockchain do just that, sort of a ‘side order’ system. Smart, huh?
Some cool layer 2 stuff includes sidechains, plasma, and state channels. They’re like friends helping out so the blockchain can run. They do the busy work so the main blockchain isn’t overwhelmed. This way, we can all play our arcade games, I mean, use blockchain, faster and without hiccups.
The Role of Sidechains, Plasma, and State Channels in Scaling
Flip the page; let’s talk sidechains. These are like mini-blockchains hitched to the main one. They function separately, so they take the load off. But they still stay connected to the main blockchain. This helps a lot with too much traffic. Imagine a busy road; now add a bike lane. That’s a sidechain for you.
Next up, plasma. It’s a big word but think of it as a special helper. Plasma creates mini blockchains too, called ‘child chains.’ These child chains can do a ton of work. Then, they send the results back to the big boss, the main blockchain. By doing this, it keeps the main blockchain neat and tidy.
Okay, what about state channels? Here’s how they roll. State channels are like tabs at a restaurant. You open one up, and you keep it running. Do lots of stuff, like pay for meals and drinks. But you only close out once at the end. That’s what state channels do. They let you do a bunch of things, like quick payments, off the main blockchain. Then, settle the total back on layer 1 later.
So, what we see now is blending layer 1 strength with layer 2 smarts. With these guys teaming up, we can handle much more, way better. It’s like having the best of both worlds. And when we talk about play – I mean, work, why not have the most fun and efficiency? Layer 2 isn’t just an upgrade; it’s a giant leap for blockchain.
Combining these scaling tricks means we get much faster transactions. But we also need to keep them cheap, secure, and like working with others. We can bring more folks to the blockchain party this way. And that’s a big win for all of us, from arcade fans to serious blockchain buffs.
Advancing Scalability and Security in Blockchain Technology
Security Aspects in Layer 1 and 2 Solutions: A Deep Dive
When we chat about blockchains, “scaling” is a big buzzword. It means making the network handle more stuff, fast. But what’s equally crucial is “security” – the muscle that protects your crypto coins from bad guys. Both Layer 1 and Layer 2 have unique ways to tackle this.
Layer 1, the blockchain’s base, focuses on security from the ground up. This includes the rules of the game, or “consensus mechanisms”, that everyone on the network follows. Think Proof of Work for Bitcoin or Proof of Stake for newer networks.
Then, enter Layer 2. These are like power-ups built on top of Layer 1, making everything faster without messing with the core rules. They work off-chain, meaning they handle transactions outside the main network. This takes the load off so Layer 1 doesn’t get too crowded.
Yet, with speed, we shouldn’t forget safety. Layer 2 scales up the pace without letting security slide. It’s like adding express lanes to a highway; the flow gets faster, but the barriers still keep everyone safe.
The Convergence of Rollups and Shard Chains: Enhancing Network Efficiency
Ever heard of traffic jams in blockchain? Well, every network can hit a limit, like roads at rush hour. To fix this, we’ve got rollups and shard chains, our heroes in cutting traffic.
Rollups gather a bunch of transactions and roll them into one. Imagine packing a bus full of people instead of cars with just one person. They then send this packed info back to Layer 1. This means fewer trips and less stress on our blockchain road.
Now, shard chains chop the network into pieces, or “shards”. Each shard is like a mini-town with its own local traffic, which means they aren’t dumping cars onto one main road. Both rollups and shard chains are smart ways we’re tweaking the system to keep transactions zippy and make sure that security is still top-notch.
These innovations are shining examples of what makes blockchain tick. Rollups and shard chains don’t just help with traffic jams; they also bake in tight security, so your crypto travels safe and sound. They work together to keep our digital towns running like well-oiled machines.
Blockchain is all about building trust, one block at a time. As we beef up our networks with Layer 1 and Layer 2 solutions, remember that scalability and security are two sides of the same coin. They go hand-in-hand to deliver a blockchain that’s not only fast and spacious but also rock-solid safe. So next time you hear about a new upgrade in the crypto world, think of it as adding more lanes to our highways or bringing in higher-tech security systems. It’s all about making blockchain ready for the whole world to hop on board.
We’ve unpacked the nuts and bolts of layer 1 blockchains and how key features like consensus methods shape their ability to handle more activity. Layer 1 and layer 2 fees, as well as their speed, can make or break user experience. But the real game changer lies in layer 2’s clever fixes that hook into the solid base layer 1 provides. By diving into layer 2 protocols, sidechains, and other technical leaps, we’ve spotted how tech gurus aim to scale up without risking security.
Now, wrapping up, it’s clear that blending smart layer 1 foundations with innovative layer 2 solutions is our best bet for a nifty, secure blockchain future. These layers aren’t rivals; they’re a duo, a tech tag team that empowers a super-fast, cost-effective network. As we watch this tech grow, remember that combining their strengths is where magic happens. Get ready, because this is just the beginning!
Q&A :
What is the difference between Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchain technologies?
Layer 1 blockchain refers to the foundational network or base architecture of blockchain technology, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. These blockchains are responsible for handling all transactions and ensuring decentralized security. Layer 2, on the other hand, is an overlaying network that builds on top of the Layer 1 blockchain. It is designed to enhance scalability and speed by handling transactions off the main chain.
How do Layer 2 solutions improve blockchain scalability?
Layer 2 solutions improve blockchain scalability by processing transactions off the main chain (Layer 1). This means that only a summarized version of these transactions is recorded on Layer 1, freeing up the network from being overwhelmed with data and thus increasing its capacity to process more transactions quickly and with lower fees. Examples of Layer 2 solutions include state channels, side chains, and rollups.
Can Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchains work together?
Yes, Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchains are designed to work together seamlessly. Layer 1 blockchains provide the fundamental security and decentralization, while Layer 2 solutions are built on top to enhance performance and scalability. By offloading some of the transactional burden to Layer 2, the two layers collaborate to provide a better balance of security, scalability, and speed.
Are Layer 2 solutions secure enough compared to Layer 1 blockchains?
Layer 2 solutions are generally considered secure, but they rely on the underlying Layer 1 blockchain for their ultimate security. While Layer 2 technologies strive to maintain similar levels of security as Layer 1, some trade-offs are made to achieve higher transaction throughput. Nevertheless, the security mechanisms and the way Layer 2 interacts with Layer 1 aim to ensure that the system as a whole remains robust against attacks.
What are some examples of Layer 2 scaling solutions?
Some popular examples of Layer 2 scaling solutions include:
- Lightning Network for Bitcoin, which enables fast and low-cost off-chain transactions.
- Plasma and Optimistic Rollups for Ethereum, which bundle many off-chain transactions into a single on-chain transaction.
- State channels, which allow users to conduct numerous transactions amongst themselves off-chain with the final state being settled on-chain.
These are just a few examples; the Layer 2 ecosystem is rich and continually evolving.