What is sharding technology? Imagine a blockchain network that is lightning fast, secure, and capable of processing millions of transactions simultaneously. This is the potential of sharding technology. However, the question remains: Is it truly secure? Let’s explore the intricate world of sharding technology and uncover its security implications.
What is sharding technology?
Sharding is a database partitioning technique that improves the scalability and performance of distributed databases. It involves splitting and storing a database’s data across multiple servers, called shards, rather than storing all the data on a single server.
The key aspects of sharding technology include data partitioning, transparent access for applications, scalability by adding more shards, high availability through shard redundancy, and query routing mechanisms to direct requests to the appropriate shard(s).
Sharding is commonly used in large-scale, high-traffic database systems, such as those found in social media platforms, e-commerce applications, and real-time analytics platforms, to handle massive amounts of data and traffic.
How does Sharding technology work?
Sharding works by partitioning a database’s data horizontally and distributing it across multiple servers, or shards. Here’s a more detailed explanation of how sharding works:
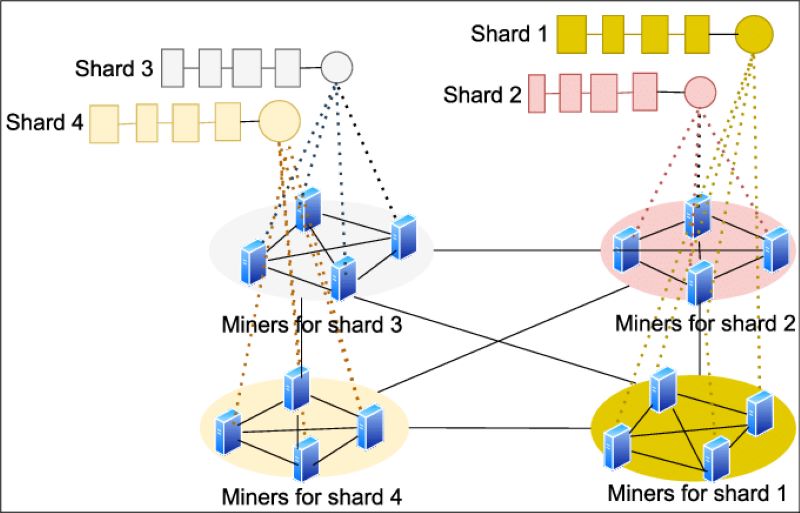
Data Partitioning: The database is partitioned into smaller, more manageable chunks of data called shards. This partitioning is typically based on a key field or attribute, such as user ID, location, or timestamp.
Shard Allocation: The shards are then allocated across multiple servers or nodes in a distributed database system. Each shard is stored on a separate server, allowing the data to be distributed across the infrastructure.
Query Routing: When an application needs to access data, it sends a query to a router or load balancer. The router determines which shard(s) contain the relevant data and routes the query to the appropriate shard(s).
Shard Management: The system manages the shards, including adding new shards, migrating data between shards, and ensuring data consistency across the sharded database.
Transparent Access: From the application’s perspective, the sharded database appears as a single, logical database. The sharding process is transparent to the end-users and applications, which interact with the database as they would a traditional, non-sharded database.
Scalability: As the data and traffic grow, additional shards can be added to the system, allowing the database to scale horizontally. This distributes the workload across more servers, improving the overall performance and capacity of the system.
High Availability: If one shard becomes unavailable, the other shards can continue serving requests, improving the overall availability of the system.
Why is Sharding technology Important?
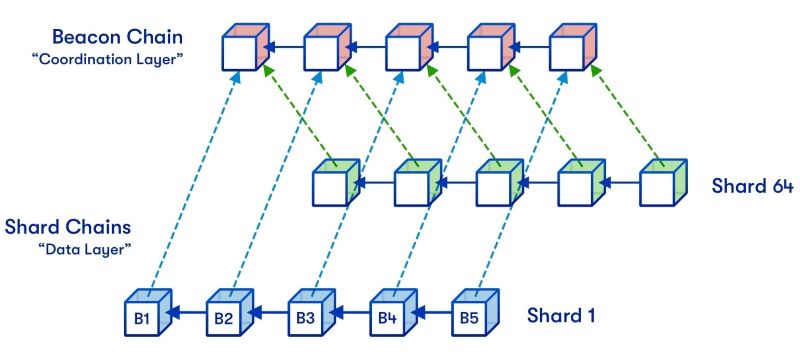
Sharding is a crucial technology for blockchain networks, as it addresses the fundamental challenge of scalability. Blockchain networks, by design, require all nodes to reach a consensus on the legitimacy of each transaction, which limits their ability to process a large number of transactions simultaneously. This is because every node in the blockchain typically retains the entire history of the network and processes every transaction, ensuring decentralization and security.
However, maintaining this decentralization and security comes at the expense of scalability. Sharded blockchains enable nodes to avoid downloading the entire history of the blockchain or validating every transaction that passes through the network, thereby improving the performance and scalability of the network. This allows blockchains to handle a greater number of users and transactions without significantly slowing down the transaction times.
The increased scalability offered by sharding has the potential to accelerate the adoption of blockchain technology across various industries, particularly in the financial sector. Fintech businesses that utilize blockchain technology may find it easier to compete with centralized payment systems if transactions can be processed more quickly.
Furthermore, sharding can enhance the accessibility of blockchain networks by reducing the hardware requirements for running a client. This can make it feasible for more individuals to participate in the network, as they can run a client on consumer devices such as personal computers or even mobile phones.
In summary, sharding is a crucial technology for blockchain networks, as it addresses the fundamental challenge of scalability, improves the performance and accessibility of the network, and has the potential to accelerate the adoption of blockchain technology across various industries.
Is sharding technology secure?
Sharding technology for blockchain networks is still in the preliminary testing phase, and its long-term security implications are not yet fully understood. There are valid concerns regarding the potential risks of sharding, which must be carefully addressed.
One key security issue is the risk of shard collision, where a shard could be taken over or overridden by malicious actors, potentially leading to the loss of information or the introduction of corrupted data into the network. This risk is mitigated in Ethereum 2.0 by the random assignment and reassignment of nodes to shards, making it difficult for attackers to target a specific shard.
Another concern is the possibility of shard corruption, where a hacker or cyber attack could gain control of a shard, potentially allowing for the introduction of fraudulent transactions. Again, Ethereum’s approach of randomly allocating and reassigning nodes to shards aims to make it challenging for attackers to identify and compromise a specific shard.
While these mitigation strategies are promising, the overall security of sharding technology remains an ongoing area of research and development. The decentralized nature of sharded blockchain networks may help to limit the impact of potential shard-level attacks, but continuous monitoring, testing, and enhancement will be necessary to ensure the long-term security and reliability of this scaling solution.
Sharding technology is a scaling solution for blockchain networks that aims to improve throughput and reduce latency by dividing the network into smaller, independent “shards.” Each shard processes a subset of the network’s transactions, allowing for parallel processing and increased scalability.
However, the security implications of sharding remain a significant concern, as the potential risks of shard collision and shard corruption must be carefully addressed. While Ethereum’s approach of random node assignment and reassignment shows promise, the long-term security of sharding technology is still an active area of research and development.
Subscribe to the Dynamic Crypto Network newsletter for expert insights and in-depth analysis.