Can blockchain networks have their cake and eat it too? Can they achieve both the lightning-fast transaction speeds needed for mass adoption and the decentralization that makes blockchain technology so revolutionary? Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a consensus mechanism that boldly claims to offer the best of both worlds, but does it live up to the hype? Let’s dive into the intricacies of DPoS and explore its potential to reshape the blockchain landscape
Overview of Blockchain Consensus
In the world of blockchain, consensus is the cornerstone of trust and security. It refers to the process by which a decentralized network of nodes agrees on a single version of truth regarding the state of the blockchain, including the validity of transactions and the order in which they are added to the chain. This agreement is crucial to ensure that all participants in the network operate on the same data, preventing double-spending and other fraudulent activities.
Traditional blockchain consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) have faced challenges in achieving both scalability and decentralization. PoW, which involves computationally intensive mining to validate transactions, consumes vast amounts of energy and can lead to centralization of power in the hands of large mining pools. PoS, while more energy-efficient, relies on the staking of tokens, which can still create barriers to entry for smaller participants.
Blockchain Consensus
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) emerges as an alternative consensus mechanism that aims to address these challenges. By introducing a system of elected delegates responsible for validating transactions and creating new blocks, DPoS strives to strike a balance between scalability, efficiency, and decentralization. However, it also raises questions about the potential for centralization of power and the need for active participation from token holders.
Understanding the nuances of blockchain consensus mechanisms is essential for comprehending the inner workings of blockchain networks and evaluating their strengths and weaknesses. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the mechanics of DPoS, its advantages and disadvantages, and its potential to reshape the blockchain landscape.
How Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) Works
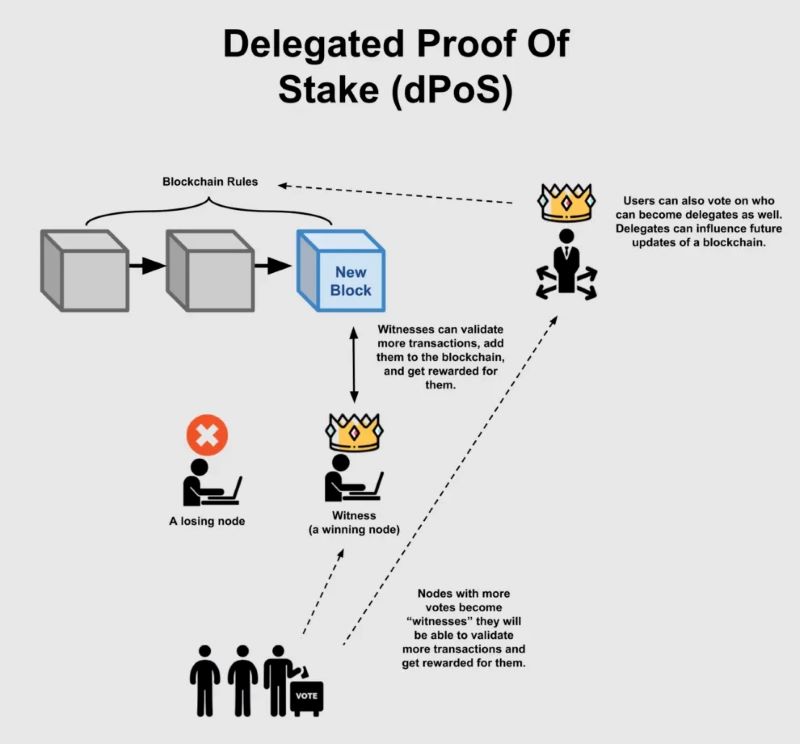
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a consensus mechanism that operates on a democratic principle, introducing a unique approach to blockchain validation and block creation. Unlike Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), where individual nodes compete to validate transactions, DPoS relies on elected delegates to perform these tasks.
Election of Delegates
In a DPoS system, token holders vote for delegates, also known as witnesses or block producers. These delegates are responsible for validating transactions and creating new blocks on the blockchain. The voting power of each token holder is typically proportional to the number of tokens they hold, allowing for a weighted voting system.
Block Production and Validation
Elected delegates take turns producing blocks and validating transactions in a round-robin fashion. This means that each delegate gets a designated time slot to propose a block of transactions, and the other delegates then verify the block’s validity. If the majority of delegates agree on the block’s correctness, it is added to the blockchain.
Incentives and Rewards
Delegates are incentivized to act honestly and efficiently through block rewards, which are typically distributed in the form of the blockchain’s native cryptocurrency. Token holders who voted for the successful delegates also receive a portion of the rewards. This creates a system where both delegates and token holders are aligned in their interest to maintain the network’s security and efficiency.
Advantages of DPoS
While Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) offers several advantages, it also presents certain challenges. One significant concern is the potential for centralization of power, as a limited number of elected delegates hold the responsibility of validating transactions and creating blocks.
This concentration of power could potentially lead to collusion or manipulation of the network. Additionally, the effectiveness of DPoS hinges on the active participation of token holders in the voting process to elect delegates. However, voter apathy can be a challenge, as not all token holders may actively engage in the governance of the network. This could lead to a situation where a small group of individuals or entities consistently dominate the delegate selection process, further exacerbating concerns about centralization.
Disadvantages and Criticisms of DPoS
Centralization Concerns: The most significant criticism of DPoS is its potential for centralization. While the system is designed to be democratic, in practice, it can lead to a scenario where a small group of delegates controls the majority of the voting power, effectively centralizing decision-making and potentially undermining the decentralized nature of the blockchain.
Security Risks: The concentration of power in a few delegates also raises security concerns. If a significant number of delegates collude, they could potentially manipulate the network for their own benefit, or even launch a 51% attack to control the blockchain.
Vote Buying and Bribery: Another concern is the potential for vote buying and bribery. Since delegates are elected based on the votes of token holders, there is a risk that delegates could try to influence the voting process through unethical means, compromising the integrity of the system.
Voter Apathy: The success of DPoS relies on the active participation of token holders in the voting process. However, voter apathy is a common issue in many DPoS systems, where only a small percentage of token holders actively participate in governance. This can further exacerbate centralization concerns.
Complexity and Technical Barriers: Implementing and maintaining a DPoS system can be complex, requiring technical expertise and resources. This can create barriers to entry for smaller projects and organizations, limiting the diversity of participants in the network.
The Future of Delegated Proof of Stake
The future of Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is poised for continued evolution and adaptation within the blockchain landscape. While it has already proven its effectiveness in achieving scalability and efficiency, ongoing research and development are focused on addressing its potential drawbacks, such as centralization concerns and voter apathy.
One potential avenue for improvement lies in the development of hybrid consensus models that combine DPoS with other mechanisms like Proof of Stake (PoS) or Proof of Authority (PoA). By leveraging the strengths of different consensus mechanisms, these hybrid models could potentially offer a more balanced approach to scalability, security, and decentralization.
Another area of focus is on enhancing the voting and governance mechanisms within DPoS systems. This could involve implementing measures to encourage broader participation from token holders, such as incentivizing voting or simplifying the voting process. Additionally, exploring innovative solutions like quadratic voting or liquid democracy could help address concerns about vote-buying and concentration of power.
As blockchain technology continues to mature and evolve, DPoS is likely to play a significant role in shaping the future of decentralized networks. Its ability to achieve high throughput and fast transaction confirmations makes it an attractive option for various applications, from decentralized finance (DeFi) to supply chain management and beyond.
Moreover, the growing interest in sustainable and energy-efficient blockchain solutions could further boost the adoption of DPoS. By eliminating the need for energy-intensive mining, DPoS offers a greener alternative to Proof of Work (PoW), aligning with the increasing demand for environmentally conscious technologies.
Overall, the future of DPoS is filled with potential. With ongoing research and development, coupled with the growing demand for scalable and sustainable blockchain solutions, DPoS is well-positioned to become a leading consensus mechanism in the years to come.
Delegated Proof of Stake offers a compelling solution for blockchain networks seeking to balance scalability, efficiency, and community engagement. While challenges like centralization concerns and voter apathy remain, the potential benefits of DPoS make it a promising avenue for further exploration and development. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, DPoS is likely to play a crucial role in shaping the future of decentralized networks.
Subscribe to Dynamic Crypto Network for in-depth analysis, expert insights, and the latest news on the ever-evolving world of blockchain technology.