Have you ever wondered what is blockchain consensus algorithm and why it matters? It’s the backbone of crypto’s secure and trusty ledger. Imagine a world where every transaction, every digital handshake, has an iron-clad agreement. That’s the power of consensus in blockchain. I’ll guide you through this crypto core, showing you how it keeps networks safe and sound. Dive in and let’s decode the secrets of blockchain consensus together.
Unraveling Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
Defining Consensus in the Blockchain Realm
A big part of blockchain’s magic is how it finds consensus. We can think of blockchain consensus as a way for a group to agree on something. It’s not just any group, though. Think of a squadron of tiny robots, each guarding its own tiny piece of digital treasure. These robots cooperate to agree on who owns what. This process seals the info onto a digital ledger. No robot can cheat or change past info. That’s how trust is born in a world without a boss.
To put it simply, consensus protocols in cryptocurrency make sure all players play fair. They’re the rules of the game. They lock in every player’s moves. Rules differ from one blockchain to another. Some are like a puzzle race, where the fastest solver wins a prize. That’s Proof of Work (PoW). Others are like a raffle, where holding more tickets gives you better odds. That’s Proof of Stake (PoS). Both keep the network safe and make sure everyone agrees on who won fair and square.
The Role of Consensus in Network Integrity and Trust
In this blockchain game, node validation is like being the ref. Nodes are like umpires that call the shots. They check each move to make sure it’s good. If a bad move tries to sneak in, nodes call it out. They keep the game clean. When the network wants to add new info, like a block of data, the nodes have to give it a thumbs up. Sometimes they don’t agree. That’s a fork. Just like in the road, they have to choose a path.
When nodes pick a path after a fork, that’s fork resolution. The nodes come back together on one track. Now the network is whole again. This is tricky but needed. Think of it as a puzzle that holds together a huge team. It’s key to making the network strong.
Mining is another word we hear a lot. It’s when people use their computers to solve tough math. This math checks and seals the blocks. Mining needs many resources, especially energy. That’s why we’re also thinking about how to do this better. We want our digital treasures without hurting the planet. This is where energy efficiency of consensus algorithms comes in.
As things grow, we need to think even bigger. More people using the network means we need it to handle more. This is scalability and consensus. Networks should work smoothly, even when they become massive cities of tiny robot guards.
In a nutshell, consensus is the heart of the blockchain. It keeps everything beating in sync. It makes blockchain a place we can trust. And as we look ahead, we wonder, “How can we make it even better?” We search for new ways to balance security and speed. Each step forward could change the digital world. Who knows what the next big move will be? But for now, one thing’s for sure: in blockchain, trust is king. And consensus is how trust lives here.
All this talk about consensus isn’t just cool, geeky stuff. It’s the core that makes sure all our digital deals are fair and safe. And that’s a big deal for everyone.
PoW vs PoS: A Comparative Analysis
Proof of Work Mechanics and Implications
Proof of Work or PoW is like a tough math quiz every computer takes to get a prize. Imagine a bunch of kids in class trying to solve a puzzle the fastest to get candy. That’s kind of how PoW blockchains work. Computers race to solve complex puzzles. The first one to solve the puzzle gets new coins, which is called mining. But PoW isn’t just about new coins. It’s about making sure everyone agrees on the ledger’s info without trusting anyone else. This trust is the core of Bitcoin and similar networks.
In PoW, mining uses a lot of power. Computers need a lot of energy to run non-stop, which makes PoW costly and not very green. Plus, as more computers join the race, puzzles get harder and need even more power. But the good part is, it’s tough for anyone to mess with the data. To change anything, you’d need lots of computers, more than half the network, and that’s really hard and pricey.
Proof of Stake Evolution and Adoption
Proof of Stake or PoS is a newer, greener way to keep the ledger in check. Instead of racing to solve puzzles, coin owners lock up some coins as a security deposit. It’s like putting your toy in the middle of the room to play a game. If you play fair, you can earn new coins, but if you cheat, you lose your toy.
PoS doesn’t need all the power like PoW, so it’s better for the planet. Networks running PoS can handle more transactions and grow without needing more power plants. Ethereum, a big network, is moving to PoS to be faster and cleaner.
Under PoS, the more coins you lock up, the better your chances to add to the ledger and earn rewards. This setup can make the rich richer but also helps keep the network safe without much power.
Both PoW and PoS help blockchains make decisions without a boss. They ensure agreement and trust between people who don’t know each other. PoW has been around longer and is tried and true. PoS is the new kid on the block, promising to keep the network safe while being kind to Earth.
As people and companies worry more about energy, PoS might become more popular. However, PoW isn’t going away fast. Networks are like big ships – they don’t turn on a dime. Deciding which is better depends on what you care about: energy, safety, or maybe both. Each method has its own path, helping us to trade and trust without a middleman. This is the power and promise of blockchain technology – a system where anyone can join, play a role, and help keep the digital world honest and secure.
The Byzantine Generals’ Problem and BFT
Exploring Byzantine Fault Tolerance and Its Importance
Imagine a group of generals planning an attack, but they must agree on a plan. It’s tough because they are far apart and some might be traitors. This is the Byzantine Generals’ Problem. In blockchain, it’s like nodes deciding on the next valid block. If nodes act weird or lie like traitors, we have a problem. But here’s where Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) comes in! It helps keep things safe even when some nodes go rogue.
BFT is key in blockchain’s security. It lets a blockchain keep working even if some nodes fail or act up. With BFT, we trust that most nodes are honest and will follow rules. It’s what lets us agree on what gets added to the blockchain. BFT is like the trust that keeps all the nodes on the same page.
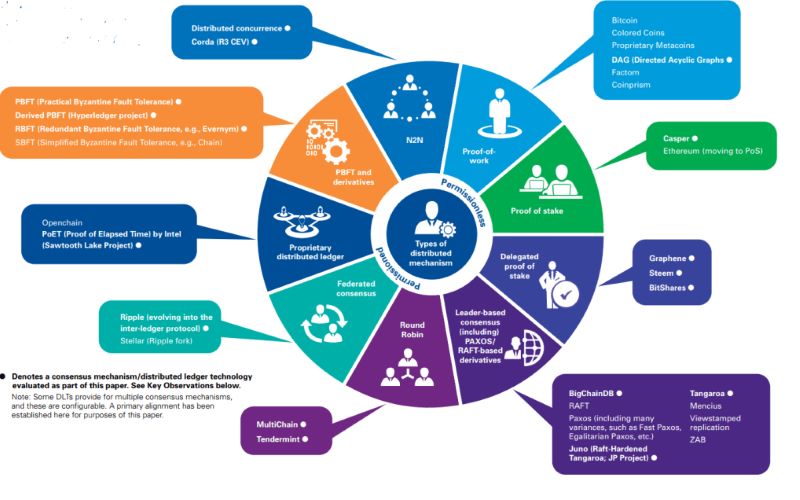
Now, BFT isn’t just one way to keep things in line. It’s a goal that lots of methods try to reach. There’s no single BFT way that everyone uses. Instead, people create different ways to get to BFT, making it fit just right for each blockchain.
Case Studies: BFT Implementation in Modern Blockchains
Let’s look at how different blockchains use BFT in real life. Some blockchains, like Ethereum, want to switch from the Proof of Work (PoW) to the Proof of Stake (PoS) model. They do this to be greener and more BFT. PoW uses a lot of energy, like a car burning gas all day long. PoS can do the same job but uses way less, like a bike instead of a car.
One more BFT type is the Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS). It works by picking a small group of nodes to agree on the next block. This is like having a small team making decisions instead of a big crowd. It’s faster and uses less power.
Another example is Ripple, which uses a sort of voting system to reach consensus without PoW mining. Their method cuts down on energy use a lot. They aim for fast and cheap transactions, and it works well for them.
Finally, let’s peek at Hyperledger. This one is a little different because it’s made just for businesses. It doesn’t use coins to keep score. Instead, it uses BFT to make sure everything is on the level. No one needs to spend a lot of energy on mining, and it keeps things very secure.
BFT in these blockchains shows us how they stand firm even when things go wrong. Whether it’s a bad node or a weird error, BFT means we can still trust in the blockchain. It’s like having a really good backup plan. The more we use it, the more secure and efficient blockchains will get. It’s all about making sure our digital stuff stays safe and sound.
Beyond Security: Performance and Sustainability
Optimizing for Scalability and Energy Efficiency in Consensus
When we talk about blockchain, the buzz is usually about security. But there’s another side to it: performance and energy use. As an expert, I spend a lot of time thinking about not just keeping blockchains safe, but also making them fast and green.
Let’s start with scalability and consensus. What do I mean by scalability? It’s about handling more users and transactions quickly. In the early days, blockchains like Bitcoin were slow. They confirmed about seven transactions a second. That’s way less than Visa does with thousands in the same time. Why? Because of the mining and consensus method called Proof of Work (PoW). It needs a lot of computational power and energy.
But here’s the thing: it’s not just about speed. It’s also about energy. The energy efficiency of consensus algorithms matters a lot. With everyone worried about climate change, we can’t ignore how much power these systems use. PoW blockchains use tons of electricity, and that’s a problem. Imagine every Bitcoin transaction using enough energy to power a house for a day!
So, what’s the solution? First, we have the Proof of Stake (PoS) algorithm. Instead of using hash power in blockchain to verify transactions, PoS uses validator nodes in blockchain. These validators are chosen based on how many coins they hold and are willing to lock up as a “stake”. This means less energy use, which is great news for our planet.
Second, we have improvements like delegated Proof of Stake and Proof of Authority mechanisms. These tweak the PoS idea to make it even more effective. Validators are picked not just for their stake, but also for how good they’ve been at keeping the network safe and speedy in the past.
The Future of Consensus Algorithms: Trends and Innovations
Now, let’s peer into the future. Like any tech, blockchain has to evolve. We’re now looking at how to mix the best parts of PoW and PoS. This blend could offer strong security while still being fast and saving energy.
New tech is also on the rise. Take Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT), for example. It’s a way to protect against failure even if some nodes try to cause trouble. That keeps transactions safe and the systems running smoothly.
Another cool area is smart contracts and consensus. This is about making contracts that can enforce themselves. They’re kind of like digital vending machines. Put in the right inputs, and out comes the result – automatically and without any need for a middleman.
We’re also seeing green blockchains. These are designed to use less energy. They might not be as big as Bitcoin or Ethereum yet, but that’s likely to change as more people call for eco-friendly tech.
So that’s the scoop on blockchain consensus. From keeping transactions secure to saving energy, there are lots of ways to improve how blockchains make decisions. With all these smart folks working on it, blockchains will get only better at serving our digital world.
In this post, we dove deep into how blockchain keeps data safe and trustworthy. We started by explaining what ‘consensus’ means in the blockchain world and why it’s key for network trust. Then, we compared Proof of Work (PoW) with Proof of Stake (PoS), talking about how they work and why people are choosing PoS more now. We also tackled the tricky Byzantine Generals’ Problem, showing how blockchains use Byzantine Fault Tolerance to avoid failure. We wrapped up by looking at how new ideas in blockchain can make it work faster and use less energy.
Thinking about all this, it’s clear: the way blockchains reach agreement is not just about keeping data secure. It’s also about making the whole system work smoother and greener for our future. As we keep inventing and learning, the tech will get even better. Keep your eye on blockchain – it’s going places, and we’re all coming along for the ride.
Q&A :
What are consensus algorithms and why are they key in blockchain technology?
Consensus algorithms are the backbone of blockchain networks, essential for ensuring all participants agree on the ledger’s true state without a central authority. They enable trust, security, and reliability in decentralized systems by providing a common method for validating transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain.
How do consensus algorithms function within a blockchain environment?
Within a blockchain, consensus algorithms facilitate agreement among distributed nodes to certify the validity of transactions. They ensure that each new transaction added to the blockchain is the only version of the truth agreed upon by all nodes, preventing fraud and avoiding the double-spending problem.
What is Proof of Work and how does it relate to blockchain consensus?
Proof of Work (PoW) is a popular consensus algorithm used by networks like Bitcoin. It involves solving complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. This process requires significant computational power, discouraging malicious actors due to the high cost of attempting to compromise the network.
Can you explain the difference between Proof of Work and Proof of Stake?
Proof of Work and Proof of Stake are both types of consensus algorithms, but they operate differently. Proof of Work requires miners to perform computationally intensive tasks, while Proof of Stake allows validators to participate and create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to ‘stake’ as collateral. Proof of Stake is considered a more energy-efficient alternative to Proof of Work.
Are there other consensus mechanisms besides PoW and PoS in blockchain systems?
Yes, beyond Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), there are other consensus mechanisms like Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), Proof of Authority (PoA), and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT). Each has its unique approach to achieving consensus on a blockchain and is tailored to specific needs and use cases of the network.